The INSANE Tutorial
This is the website for the Middleware 2025 tutorial: "This is INSANE! Kernel-Bypass Networking Finally Made Easy". The website contains the material for the tutorial, including slides, pointers to the code repository, and additional resources.
Tutorial repository: https://github.com/ellerre/insane-tutorial (contains the code and the instructions for the hands-on session)
INSANE repository: https://github.com/MMw-Unibo/INSANE
Slides:
Overview
This tutorial aims to lower the entry barrier for developers and researchers interested in exploiting kernel-bypass networking and modern acceleration frameworks. Its goal is to provide participants with both the conceptual foundations and the practical skills needed to build portable, high-performance communication systems using the INSANE middleware, thereby minimizing the need for hardware-specific programming and manual tuning. By combining theoretical background with practical experimentation, the tutorial aims to engage both academics seeking insight into emerging research directions and professionals looking for effective ways to integrate advanced networking into real systems.
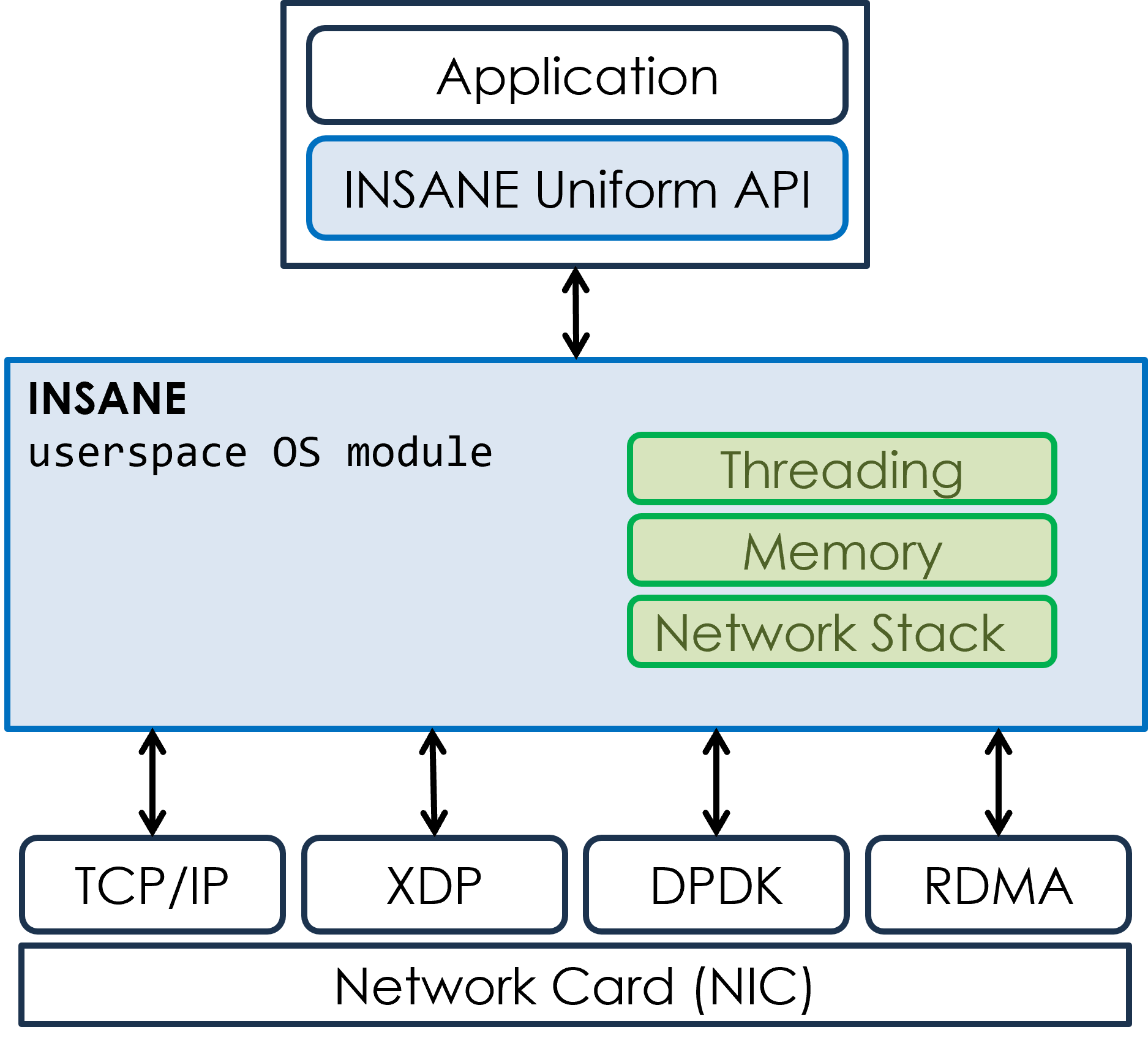
Target Audience. The tutorial is intended for researchers, practitioners, and developers interested in the design and deployment of modern distributed systems and middleware. It will appeal to those working in cloud, edge, and networked computing, as well as in domains such as telecommunications, industrial automation, and data-intensive services, where communication performance is increasingly critical. Participants are not required to have prior experience with kernel-bypass or hardware acceleration, but a general familiarity with networking concepts and middleware frameworks (e.g., MQTT, DDS, or NATS) will help in following the examples.
Materials and Setup The tutorial materials, will remain online for future reference. Participants interested in joining the hands-on session should bring a laptop with SSH capabilities and, optionally, a code editor of their choice. During the session, they will modify and execute Python or C code on remote machines to observe the performance impact of different networking configurations.
Motivation and Background
Recent years have seen a major shift in networking, driven by the rapid evolution of hardware, software stacks, and compilers. Modern Network Interface Cards (NICs) have become programmable accelerators, with SmartNICs and RDMA-capable devices executing parts of the data path directly on hardware. In parallel, kernel-bypass frameworks such as the Data Plane Development Kit (DPDK) and the Linux eBPF eXpress Data Path (XDP), along with compiler-assisted optimizations, have drastically reduced the overhead of traditional OS networking. Together, these advances enable microsecond scale latencies and tens of gigabits of throughput on commodity systems. Yet, their adoption remains difficult: acceleration frameworks are heterogeneous, hardware-specific, and exposed through low-level APIs that demand expert tuning. As a result, despite their maturity, these technologies remain hard to integrate into higher-level systems, highlighting the need for middleware services that can make advanced networking both portable and easy to use. Such middleware is increasingly critical for applications in domains like real-time control loops, AI-driven analytics, and next-generation telecommunications, which demand highly variable yet stringent Quality of Service (QoS) requirements in terms of latency and bandwidth
INSANE is a data-centric middleware designed to make advanced network acceleration accessible through a simple, portable interface. It lets developers specify high-level QoS requirements, which are dynamically mapped to the most appropriate networking backend, such as DPDK, XDP, or RDMA, without modifying application code. Built on a sidecar architecture, INSANE runs a lightweight daemon on the applications' hosting machines to manage communication through shared memory and modular plugins, ensuring zero-copy transfers and minimal overhead. Unlike existing middleware solutions such as MQTT, DDS, or NATS, which rely on conventional kernel-based networking and cannot transparently exploit hardware offloading or kernel-bypass stacks, INSANE was conceived from the ground up to integrate these capabilities while preserving ease of use and portability. The new version 2 extends this foundation with broader language support, including a Python API, improved observability, and enhanced cloud-based deployment tools such as Kubernetes integration, offering a mature, efficient bridge between application-level data distribution and the evolving ecosystem of accelerated networking technologies.
Tutorial Outline
The tutorial, lasting approximately three hours, is structured in three progressive parts that blend conceptual grounding with practical experience:
- Part 1 (45 min): Background on network acceleration technologies and their evolution across hardware, software, and compilers.
- Part 2 (30 min): Overview of the INSANE middleware and its architecture, design goals, and version 2 improvements.
- Part 3 (90 min): Hands-on demonstration of INSANE in practice, using an application based on NATS as a reference.
Part 1 - Network Acceleration Background
The first part introduces participants to the current landscape of network acceleration options, explaining how hardware and software advances, such as SmartNICs, RDMA, DPDK, and XDP, are reshaping communication performance in distributed systems. It will discuss how these technologies emerged from the limitations of traditional OS networking, how compiler and framework innovations have contributed to closing the performance gap, and why exploiting these solutions remains complex in practice. This introduction will provide the background needed to appreciate the motivation and application domains for middleware like INSANE.
Part 2 - The INSANE Middleware
The second part will focus on the INSANE middleware itself. Participants will be guided through its rationale and architecture, seeing how it abstracts heterogeneous network stacks through a unified data-centric API and a lightweight sidecar runtime. The session will present the main concepts of streams, QoS policies, and backend selection, along with the new features of version 2, including its Python interface and improved observability tools. The session will also present relevant related work that has been presented recently on this topic and motivate why INSANE presents unique design choices that makes it suitable for diverse application domains.
Part 3 - Hands-on Session
The final part will be a hands-on session where participants put theory into practice through guided examples showing how INSANE can be integrated into different application domains, with the level of depth adapted to participants' interests. The exercise will begin with a simple application built on the well-known NATS middleware, whose communication layer will be progressively replaced with INSANE calls to demonstrate how advanced acceleration can be achieved with minimal code changes. Participants will evaluate performance improvements and observe how the middleware selects kernel-bypassing technologies based on user-specified requirements. Depending on audience engagement, the session may conclude with more advanced demonstrations of more complex INSANE-based applications that further highlight its flexibility and portability across diverse environments.
Speaker

Lorenzo Rosa
Lorenzo Rosa is a Postdoctoral Researcher at the University of Bologna, Italy, where he obtained a PhD in Computer Science and Engineering (2024). His research interests include cloud and edge computing, serverless computing, communication middleware, and industrial networking. His work focuses on systems performance, particularly on Quality of Service (QoS) concerns and host network performance. His research in this area has led to several publications, including at IEEE ICDCS 2022 and ACM Middleware 2023, as well as a forthcoming survey in IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials. Dr. Rosa also has extensive teaching experience as a teaching assistant for courses including Computer Networks and Foundations of Computer Science at the University of Bologna. He is the main designer and developer of INSANE.